SECONDARY PROCESSING
Product Structural Design Secondary Processing Specifications - Laser Engraving
(I) Concept
Laser engraving, or marking, relies on the large energy density within the laser beam to achieve the surface etching effect of the material. It is applicable to all metals, plastics, wood, glass, and part of the colored metals. Its features are high precision, fast speed, and intricate and durable effects.
(II) Processing principle
Laser Generation: It is a very concentrated beam of light which, with the aid of a laser device, is generated. Depending on processing requirements and the type of laser device, it can be continuous or pulsed.
Focusing the beam: The laser beam is guided and focused through a series of optical components, such as lenses and mirrors, into an extremely small location on the surface of the material. The size of this spot determines the fineness of the engraving.
Material Processing: When the focused laser beam falls onto the material's surface, it gets absorbed within a very short period of time. Due to this absorption, the temperature of the material rises at an alarming rate. This considerable temperature can result in various physical or chemical changes in the material, including evaporation. Laser energy may instantly cause evaporation in volatile materials, forming gas.
Melting and Solidification: When the energy created by a laser is applied, it will melt the surface of those materials with a high melting point, which then solidifies quickly to form marks or patterns.
Chemical Reactions: Sometimes, the energy of the laser can bring about chemical reactions on the surface of the material, either in coloration or structural changes.
Control Movement: A control system usually guides the movement of the laser beam to form patterns or texts on the surface of the material. It may be computer-controlled, moving precisely the laser beam according to the design pattern to "draw" on the material's surface what is required.
(III) Laser Engraving Machine
These are devices that use the laser beam to make permanent marks at the surface or inside transparent materials. The laser beam is capable of producing physical or chemical effects in materials and can create marks, patterns, or texts; hence, it is also called a laser marking machine or laser engraving machine.
(IV) Case Analysis
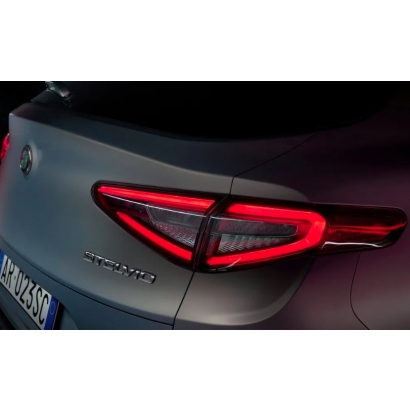
Laser engraving, also referred to as laser marking or laser etching, applies optical principles in its surface treatment process. This process is often applied to mobile phones and electronic dictionary keys. For instance:
Keyboard Production: Different colored oil is sprayed onto the keys, and then a white layer is sprayed overall. Laser engraving scrubs off the white layer, revealing a layer of colored layers that show the colorful keys.
TRANSPARENCY KEYBOARDS The materials are made of PC or PMMA, and a layer of oil is first sprayed on top, followed by laser engraving a text portion to let light pass from the bottom in order to give out a transparent effect.
(V) Working Method
By the way of engraving, laser engraving can be divided into dot matrix engraving and vector cutting:
Dot Matrix Engraving: The swinging of the laser head is similar to high-definition dot matrix printing, moving left and right. Every time, it makes a line composed of a series of dots. The laser head makes several lines up and down to form an integral image or text.
Vector Cutting: This is quite the opposite of dot matrix engraving. The process is done along the outline of the graphic. This mode is majorly applied for cutting through materials such as wood, paper, and acrylic. It can also mark the surface of various materials.
(VI) Performance
Engraving speed, engraving intensity, and spot size are the three most important factors that determine the performance of a laser engraving machine.
Speed: This is the laser head's speed, normally expressed in inches per second, which is defined as the rate at which it travels. High speed can increase production efficiency or control the depth of cut or engraving. Intensity: This relates to the strength or power of the laser, usually stating that the larger the number, the deeper one will be cutting or engraving.
Lens size: is set by lenses of different focal lengths. The smaller the spot, the more suitable for high-resolution engraving; larger spots are better suited for lower resolutions but optimal for vector engraving. The lens configuration is normally standard at 2.0 inches.
(VII) Applicable Materials
It can be engraved on the following materials: bamboo; wood products; acrylic; metal plates; glass; stone; crystal; Corian; paper; two-color plates; aluminum oxide; leather; plastic; epoxy resin; polyester resin; and coated metals.
(VIII) Safety protection
Hazards
Laser damage: Eyes and skin can be damaged by VLT& NIR; some UV wavelengths can be carcinogenic.
Chemical damage: Toxic particles or gases
Electrical damage: High voltage or high current from laser power supply
Safety levels
Class I: No hazard laser systems, below 0.4 mW
Class II: Low-intensity visible light laser systems, 0.4 mW~1 mW
Class III: Medium-intensity laser systems
Class IIIa: Not hazardous to unprotected eyes but hazardous when focused, 1.0 mW~5 mW
Class IIIb: No hazardous diffuse reflections, 5.0 mW~500 mW
Class IV: High-power laser system, above 500 mW
Protective Measures
Avoid direct eye exposure to the laser beam.
Use warning signs.
Only experienced personnel should operate the laser.
Enclose the beam path to prevent leakage.
Wear appropriate protective eyewear.
Avoid placing body parts in the beam or reflection areas.
Remove unnecessary reflective objects from the work area.
Provide appropriate shielding around the workpiece.
Set up the laser system to avoid direct eye level placement.
Ensure proper ventilation and exhaust in the work environment (wear masks during operation).
Be aware of high voltage in the laser power supply to prevent electric shock.
(IX) Laser Engraving Steps
Design: Use special software to make the pattern or text wanted and then change it into a form that the laser engraving machine will understand. Positioning involves the material being put in the correct position within the laser engraving machine. The material also has to be held firmly in place. Engrave: After designing and positioning, start the laser engraving machine, and it will do what has been designed accordingly.
Post-processing: Clean the material or perform other post-processing to obtain the desired effect after engraving.
Applications
It has a very wide application in Laser Engraving:
Signage Production: Company logos, product labels.
Personalized Customization: Personalized gifts, souvenirs.
Craft Making: Wood carving, stone carving.
Electronics Industry: Circuit board engraving, precision component processing.
Owing to its high precision and durability, laser engraving has become one of the key technologies in many industries.
Laser engraving, or marking, relies on the large energy density within the laser beam to achieve the surface etching effect of the material. It is applicable to all metals, plastics, wood, glass, and part of the colored metals. Its features are high precision, fast speed, and intricate and durable effects.
(II) Processing principle
Laser Generation: It is a very concentrated beam of light which, with the aid of a laser device, is generated. Depending on processing requirements and the type of laser device, it can be continuous or pulsed.
Focusing the beam: The laser beam is guided and focused through a series of optical components, such as lenses and mirrors, into an extremely small location on the surface of the material. The size of this spot determines the fineness of the engraving.
Material Processing: When the focused laser beam falls onto the material's surface, it gets absorbed within a very short period of time. Due to this absorption, the temperature of the material rises at an alarming rate. This considerable temperature can result in various physical or chemical changes in the material, including evaporation. Laser energy may instantly cause evaporation in volatile materials, forming gas.
Melting and Solidification: When the energy created by a laser is applied, it will melt the surface of those materials with a high melting point, which then solidifies quickly to form marks or patterns.
Chemical Reactions: Sometimes, the energy of the laser can bring about chemical reactions on the surface of the material, either in coloration or structural changes.
Control Movement: A control system usually guides the movement of the laser beam to form patterns or texts on the surface of the material. It may be computer-controlled, moving precisely the laser beam according to the design pattern to "draw" on the material's surface what is required.
(III) Laser Engraving Machine
These are devices that use the laser beam to make permanent marks at the surface or inside transparent materials. The laser beam is capable of producing physical or chemical effects in materials and can create marks, patterns, or texts; hence, it is also called a laser marking machine or laser engraving machine.
(IV) Case Analysis
Laser engraving, also referred to as laser marking or laser etching, applies optical principles in its surface treatment process. This process is often applied to mobile phones and electronic dictionary keys. For instance:
Keyboard Production: Different colored oil is sprayed onto the keys, and then a white layer is sprayed overall. Laser engraving scrubs off the white layer, revealing a layer of colored layers that show the colorful keys.
TRANSPARENCY KEYBOARDS The materials are made of PC or PMMA, and a layer of oil is first sprayed on top, followed by laser engraving a text portion to let light pass from the bottom in order to give out a transparent effect.
(V) Working Method
By the way of engraving, laser engraving can be divided into dot matrix engraving and vector cutting:
Dot Matrix Engraving: The swinging of the laser head is similar to high-definition dot matrix printing, moving left and right. Every time, it makes a line composed of a series of dots. The laser head makes several lines up and down to form an integral image or text.
Vector Cutting: This is quite the opposite of dot matrix engraving. The process is done along the outline of the graphic. This mode is majorly applied for cutting through materials such as wood, paper, and acrylic. It can also mark the surface of various materials.
(VI) Performance
Engraving speed, engraving intensity, and spot size are the three most important factors that determine the performance of a laser engraving machine.
Speed: This is the laser head's speed, normally expressed in inches per second, which is defined as the rate at which it travels. High speed can increase production efficiency or control the depth of cut or engraving. Intensity: This relates to the strength or power of the laser, usually stating that the larger the number, the deeper one will be cutting or engraving.
Lens size: is set by lenses of different focal lengths. The smaller the spot, the more suitable for high-resolution engraving; larger spots are better suited for lower resolutions but optimal for vector engraving. The lens configuration is normally standard at 2.0 inches.
(VII) Applicable Materials
It can be engraved on the following materials: bamboo; wood products; acrylic; metal plates; glass; stone; crystal; Corian; paper; two-color plates; aluminum oxide; leather; plastic; epoxy resin; polyester resin; and coated metals.
(VIII) Safety protection
Hazards
Laser damage: Eyes and skin can be damaged by VLT& NIR; some UV wavelengths can be carcinogenic.
Chemical damage: Toxic particles or gases
Electrical damage: High voltage or high current from laser power supply
Safety levels
Class I: No hazard laser systems, below 0.4 mW
Class II: Low-intensity visible light laser systems, 0.4 mW~1 mW
Class III: Medium-intensity laser systems
Class IIIa: Not hazardous to unprotected eyes but hazardous when focused, 1.0 mW~5 mW
Class IIIb: No hazardous diffuse reflections, 5.0 mW~500 mW
Class IV: High-power laser system, above 500 mW
Protective Measures
Avoid direct eye exposure to the laser beam.
Use warning signs.
Only experienced personnel should operate the laser.
Enclose the beam path to prevent leakage.
Wear appropriate protective eyewear.
Avoid placing body parts in the beam or reflection areas.
Remove unnecessary reflective objects from the work area.
Provide appropriate shielding around the workpiece.
Set up the laser system to avoid direct eye level placement.
Ensure proper ventilation and exhaust in the work environment (wear masks during operation).
Be aware of high voltage in the laser power supply to prevent electric shock.
(IX) Laser Engraving Steps
Design: Use special software to make the pattern or text wanted and then change it into a form that the laser engraving machine will understand. Positioning involves the material being put in the correct position within the laser engraving machine. The material also has to be held firmly in place. Engrave: After designing and positioning, start the laser engraving machine, and it will do what has been designed accordingly.
Post-processing: Clean the material or perform other post-processing to obtain the desired effect after engraving.
Applications
It has a very wide application in Laser Engraving:
Signage Production: Company logos, product labels.
Personalized Customization: Personalized gifts, souvenirs.
Craft Making: Wood carving, stone carving.
Electronics Industry: Circuit board engraving, precision component processing.
Owing to its high precision and durability, laser engraving has become one of the key technologies in many industries.