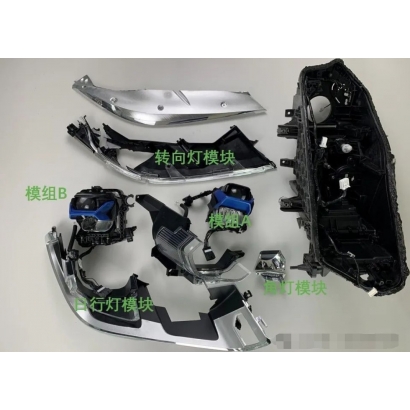
OEM/ODM
Automotive Lighting Internal Structure Design
Internal Structure Design of Automotive Lighting
The internal structure design in automotive lighting is a strict and complex engineering process, as it includes many components to deliver functions such as illumination, heat dissipation, sealing, and vibration resistance. The detailed knowledge on the internal structure design of automotive lighting is given below.
1. Light Source Module
LED Module: Most of the automotive lighting, which has been in use today, is used as a source of light LEDs. This shall ensure that the LED modules have a good heat dissipation design for long service life and stable operation. Common designs to dissipate heat are normally aluminum heat sinks and materials with high thermal conductivity.
Light Source Socket: Used for fixing the light source position to hold the light source stably and conveniently for replacement. The bulb socket is usually made from high-temperature-resistant materials.
2. Optical Design
Reflectors and Lenses: These are used to concentrate and steer light in such a way as to realize the required lighting effect. Normally, reflectors will be plastic or metal with a coating of silver or aluminum, and the lenses likely contain plastics of high transparency like PC (polycarbonate) or PMMA (polymethyl methacrylate).
Optical Engine: Bin of LEDs and lenses to shape the light beam and throw light.
3. Thermal Management Design
Heat Sinks: This is the part of the system that absorbs the heat and dissipates it as it builds while the light source is running. Heat sinks used in LED lights are typically of aluminum alloy material.
Thermal Conductive Materials: Fine materials of high efficiency of thermal conductivity are installed between the LED module and the heat sink to improve efficiency in heat dissipation.
4. Circuit Design
Driving Circuit: It is used to switch, brighten, and change modes of the light source. Equipped with overheat protection, over-voltage protection, and short circuit protection functions.
Connectors: Connect the inner circuit of the Light with the vehicle circuit; to ensure a stable power supply.
5. Sealing and Waterproof Design
Sealing Rings: Used to seal between different parts of the Light, to prevent water and dust from entering. Common materials are Silicone and Rubber.
Waterproof Breathable Valves: Balances the pressure difference between the inside and outside of the Light. Prevents water vapor from entering and allows internal air to escape.
6. Mounting Structure
Mounting Brackets: Fixing the light on the vehicle body, holding its position fixed. Most mounting brackets need to have anti-vibration functions to adapt to vibrations in the course of vehicle operation.
Adjustment Mechanisms: Some lights are designed with angle adjustment mechanisms that enable adjusting the angles and directions of light to meet different lighting demands.
7. Housing and Decorative Parts
Light Housing: Houses the internal components and is normally made of heat-resistant UV-resistant plastic, such as PC or PMMA, or even glass.
Decorative Frames: Beautify the light and offer additional protection.
8. Safety and Testing
Standard Compliance: The light design should be according to international standards, such as ECE or DOT, and pass all the related safety requirements for on-road applications.
Testing and Validation: Optical performance, heat dissipation resistance, durability, and waterproofing, among other things, are tested to guarantee product quality and performance steadiness.
Designing an interior structure of automotive lamps involves comprehensive optical, thermal, electrical, and mechanical features. This will require an accurate design and a very strict test to make sure that its performance and durability meet the standards.
The internal structure design in automotive lighting is a strict and complex engineering process, as it includes many components to deliver functions such as illumination, heat dissipation, sealing, and vibration resistance. The detailed knowledge on the internal structure design of automotive lighting is given below.
1. Light Source Module
LED Module: Most of the automotive lighting, which has been in use today, is used as a source of light LEDs. This shall ensure that the LED modules have a good heat dissipation design for long service life and stable operation. Common designs to dissipate heat are normally aluminum heat sinks and materials with high thermal conductivity.
Light Source Socket: Used for fixing the light source position to hold the light source stably and conveniently for replacement. The bulb socket is usually made from high-temperature-resistant materials.
2. Optical Design
Reflectors and Lenses: These are used to concentrate and steer light in such a way as to realize the required lighting effect. Normally, reflectors will be plastic or metal with a coating of silver or aluminum, and the lenses likely contain plastics of high transparency like PC (polycarbonate) or PMMA (polymethyl methacrylate).
Optical Engine: Bin of LEDs and lenses to shape the light beam and throw light.
3. Thermal Management Design
Heat Sinks: This is the part of the system that absorbs the heat and dissipates it as it builds while the light source is running. Heat sinks used in LED lights are typically of aluminum alloy material.
Thermal Conductive Materials: Fine materials of high efficiency of thermal conductivity are installed between the LED module and the heat sink to improve efficiency in heat dissipation.
4. Circuit Design
Driving Circuit: It is used to switch, brighten, and change modes of the light source. Equipped with overheat protection, over-voltage protection, and short circuit protection functions.
Connectors: Connect the inner circuit of the Light with the vehicle circuit; to ensure a stable power supply.
5. Sealing and Waterproof Design
Sealing Rings: Used to seal between different parts of the Light, to prevent water and dust from entering. Common materials are Silicone and Rubber.
Waterproof Breathable Valves: Balances the pressure difference between the inside and outside of the Light. Prevents water vapor from entering and allows internal air to escape.
6. Mounting Structure
Mounting Brackets: Fixing the light on the vehicle body, holding its position fixed. Most mounting brackets need to have anti-vibration functions to adapt to vibrations in the course of vehicle operation.
Adjustment Mechanisms: Some lights are designed with angle adjustment mechanisms that enable adjusting the angles and directions of light to meet different lighting demands.
7. Housing and Decorative Parts
Light Housing: Houses the internal components and is normally made of heat-resistant UV-resistant plastic, such as PC or PMMA, or even glass.
Decorative Frames: Beautify the light and offer additional protection.
8. Safety and Testing
Standard Compliance: The light design should be according to international standards, such as ECE or DOT, and pass all the related safety requirements for on-road applications.
Testing and Validation: Optical performance, heat dissipation resistance, durability, and waterproofing, among other things, are tested to guarantee product quality and performance steadiness.
Designing an interior structure of automotive lamps involves comprehensive optical, thermal, electrical, and mechanical features. This will require an accurate design and a very strict test to make sure that its performance and durability meet the standards.