Product Design Specifications - Nut Embedding Process
Chapter 1: Overview
1.1 Overview
Plastic embedded nuts, also known as hot-pressed nuts or hot-melt nuts, are a highly effective and rapid technology for enhancing internal threads in plastic parts. Embedded nuts significantly increase the torque and pull-out strength of plastic parts and simplify mold structures, making them widely used in plastic product design.
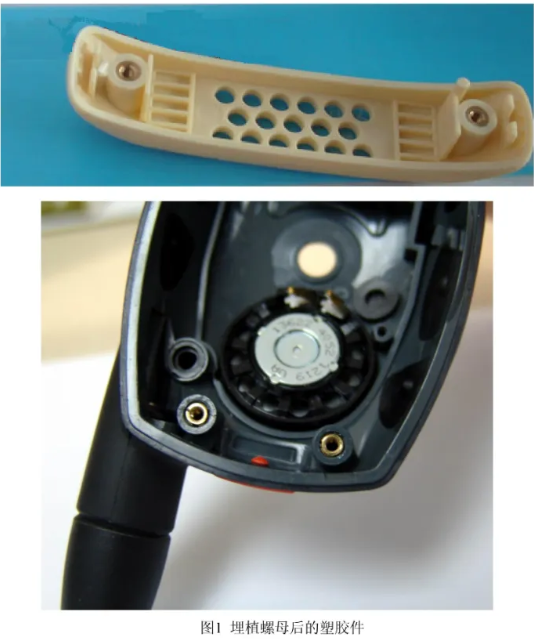

1.2 Advantages of Embedded Nuts
- Ease of Assembly and Disassembly
- High Torque and Pull-Out Strength
- High Locking Force
- Compact Design: Simple stud structure
1.3 Nut Structural Features
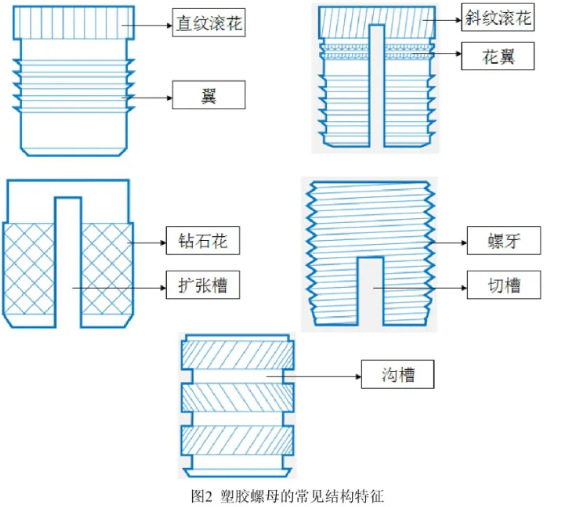
- Straight Knurling: Good torque performance but poor pull-out strength.
- Diagonal Knurling: Smaller knurling area and depth, easier to control, good balance of torque and pull-out strength.
- Diamond Knurling: Larger knurling area, shallow knurling, challenging to control embedding process, performs well in ultrasonic embedding.
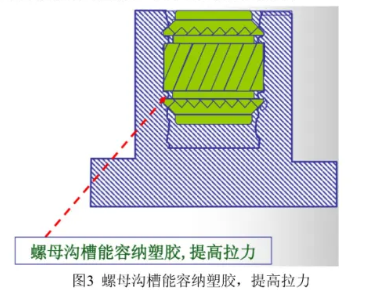
- Grooves: Accommodate plastic, provide pull-out strength.
- Wings and Flanges: Increase pull-out strength.
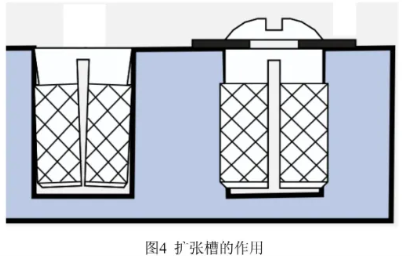
- Expansion Slots: Provide deformation space during embedding.
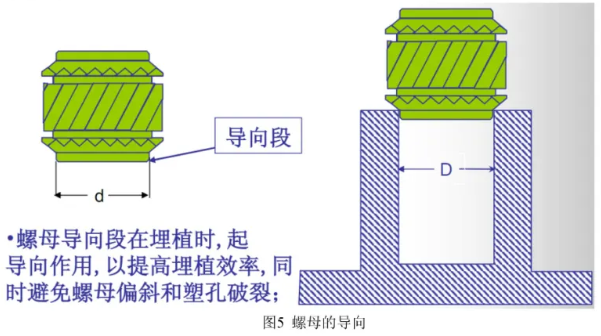
1.4 Nut Guidance
Good guidance is essential during embedding to enhance efficiency and avoid misalignment or breakage. Typically, the nut has chamfered edges to provide guidance, so no additional chamfering on the plastic stud is required.
1.5 Common Nut Materials
- Brass
- Carbon Steel
- Stainless Steel
- Aluminum Alloy
Brass is the most commonly used due to its high thermal conductivity and good machinability.
1.6 Nut Embedding Methods
-
Injection Molding Nut
- Insert the brass nut into the mold before injection molding. Different shrinkage rates between the nut and plastic can cause residual stress, and the process is less efficient.
-
Hot-Pressing Nut
- Heat the brass nut to a certain temperature to soften the plastic, then press it in. This method produces less internal stress and provides good torque and pull-out strength. Commonly performed using hot-pressing machines or manual soldering irons.
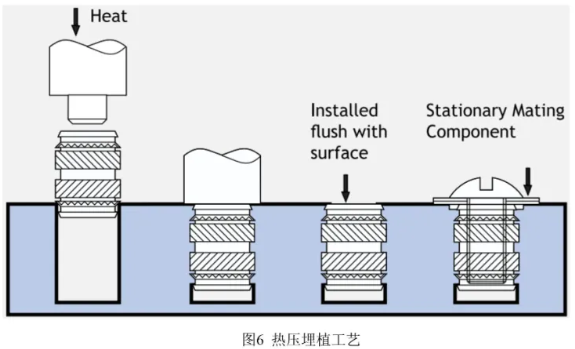
Key Parameters:
- Hot-Press Head Temperature
- Preheat Time
- Embedding Time
- Heat the brass nut to a certain temperature to soften the plastic, then press it in. This method produces less internal stress and provides good torque and pull-out strength. Commonly performed using hot-pressing machines or manual soldering irons.
-
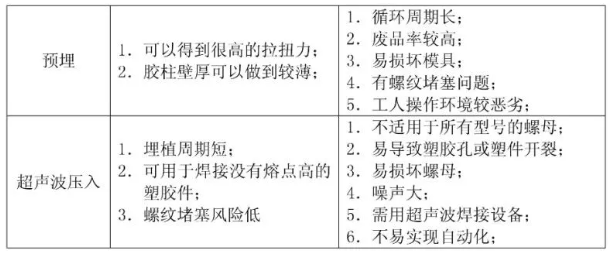
Ultrasonic Nut
- Ultrasonic embedding uses vibrations to increase the temperature at the interface between the nut and plastic, embedding the nut when the temperature reaches the plastic's softening point. After vibration stops, the part cools under pressure.
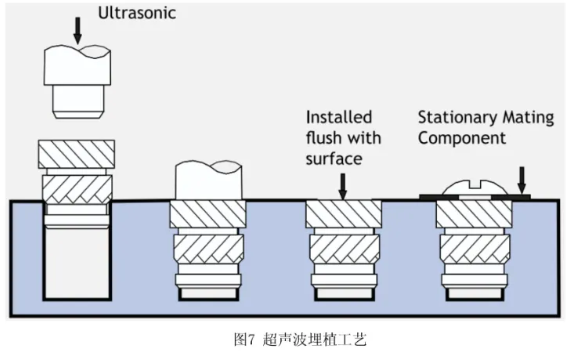
Key Parameters:
- Ultrasonic Frequency: 20-80 kHz
- Amplitude: 40-100 µm
- Vibration Time
Note: Ultrasonic embedding can damage the nut, especially the threaded parts. It is not recommended for nuts smaller than M1.6.
- Ultrasonic embedding uses vibrations to increase the temperature at the interface between the nut and plastic, embedding the nut when the temperature reaches the plastic's softening point. After vibration stops, the part cools under pressure.
-
Cold-Pressing
- Embed the nut directly into the plastic using pressure without heating. This method is less effective for torque and pull-out strength, suitable for applications with low stress.
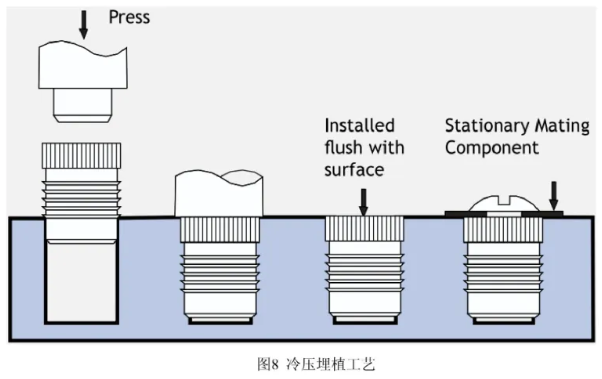
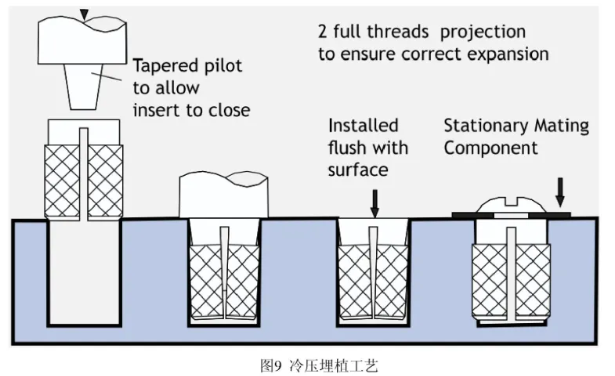
- Embed the nut directly into the plastic using pressure without heating. This method is less effective for torque and pull-out strength, suitable for applications with low stress.
-
Self-Tapping
- Screw the nut into the plastic to create a threaded section.
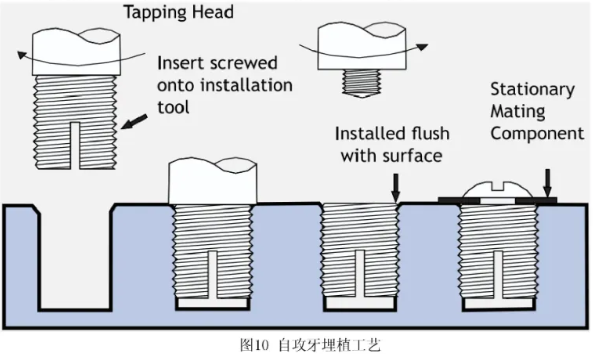
- Screw the nut into the plastic to create a threaded section.
Commonly Used Methods: Hot-pressing, in-mold pre-embedding, and ultrasonic embedding.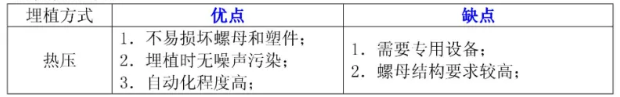
1.7 Factors Affecting Hot-Press Nut Quality
-
Design
- Nut type selection
- Plastic stud structure design
-
Process
- Injection molding process
- Hot-pressing process
Chapter 2: PSM Plastic Nuts Introduction and Application
PSM and other brands like PEM and Dodge offer a variety of plastic nuts. Domestic manufacturers include Suzhou Fanwo Industrial Fasteners Co., Ltd. and Shenzhen Lifang Precision Hardware Co., Ltd.
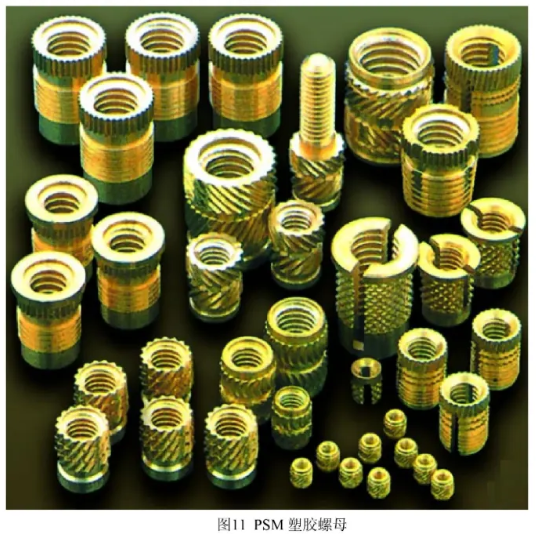

2.1 PSM Plastic Embedded Nuts Overview
- Thermoplastic Nuts: Suitable for hot-pressing, ultrasonic embedding, cold-pressing, or self-tapping.
- Thermosetting Plastic Nuts: Specific embedding methods and nut types available.
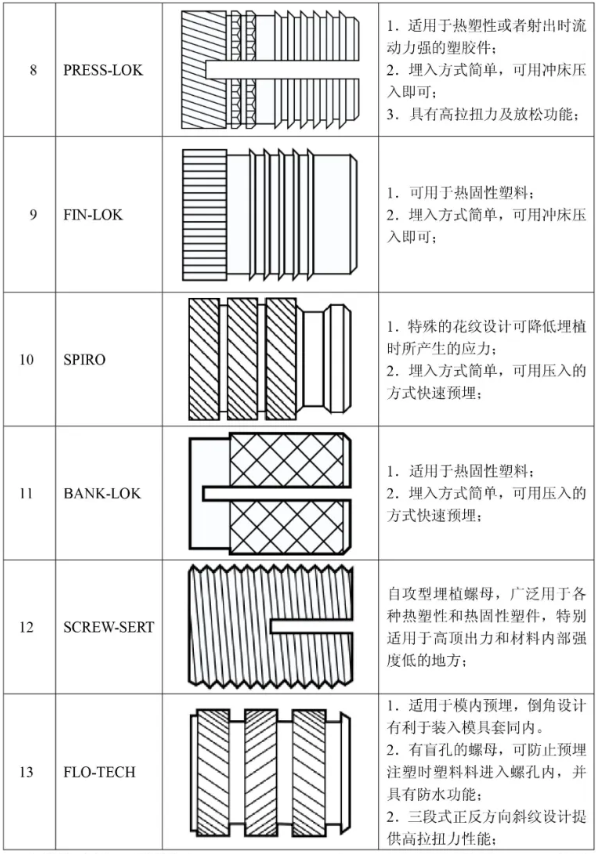
2.2 Types of PSM Nuts and Their Features
-
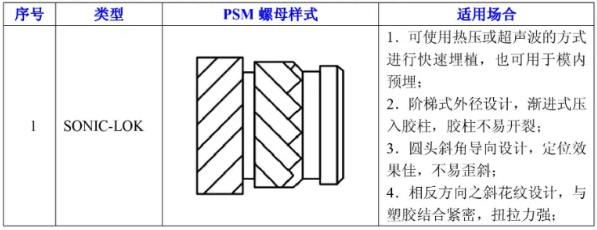
TECH-SONIC Nuts
- Features: Non-directional shape, high torque performance, suitable for thin plastic studs.
- Design Notes: Follow specific wall thickness and hole depth guidelines.
-
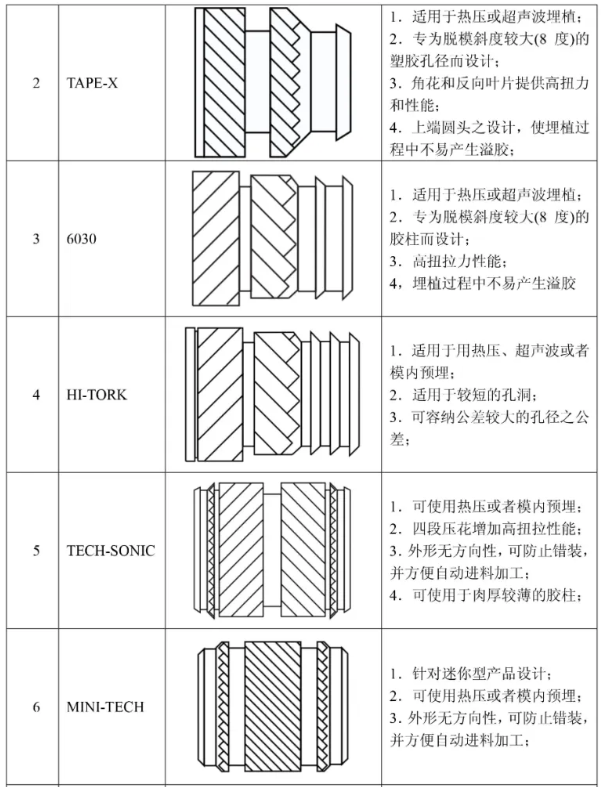
MINI-TECH Nuts
- Features: Suitable for small products, prevents thread stripping, non-directional for easy automation.
-
FLO-TECH Nuts
- Features: Blind hole design prevents plastic from entering threads, anti-water, and easy mold insertion.
-
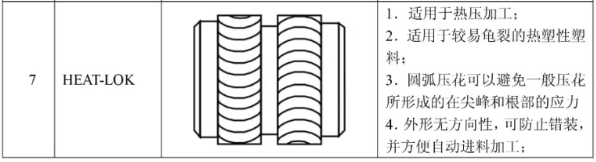
HEAT-LOK Nuts
- Features: High torque performance, suitable for heat-sensitive non-crystalline plastics.
- Features: High torque performance, suitable for heat-sensitive non-crystalline plastics.
Material Selection:
- Crystalline Plastics: Any nut type can be used.
- Non-Crystalline Plastics: Avoid sharp knurling; opt for precise nuts or perform pre-plating before embedding.
Recommended Methods for Common Materials:
- ABS: Pre-embedding or hot-pressing, TECH-SONIC recommended.
- PC+ABS: Hot-pressing recommended, TECH-SONIC or FLO-TECH nuts.
- PC: Avoid in-mold pre-embedding due to stress; use hot-pressing with TECH-SONIC nuts.
- Small Products: MINI-TECH nuts for space-saving.
Chapter 3: Hot-Press Nut Processing Technology
3.1 Hot-Press Temperature Selection
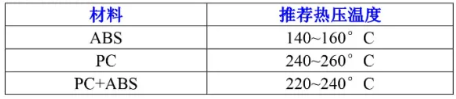
- Choose a temperature 10-20°C below the plastic melting point. Recommended temperatures for common materials provided in the table.
3.2 Hot-Press Equipment
- Hot-Press Machines: Stable process, capable of embedding multiple nuts at once, high initial cost, requires special fixtures.

- Soldering Irons: Suitable for manual embedding, lower cost, less stable process.
3.3 Hot-Press Operation
- Key Points:
- Heat the nut for 7-10 seconds before pressing.
- Avoid excessive pressure and premature embedding.
- Check that the nut is level with the plastic surface and no swelling or cracking.
3.4 Plastic Material Impact
- Crystalline Plastics: Avoid in-mold pre-embedding.
- Non-Crystalline Plastics: Prefer hot-pressing to avoid internal stress and cracking.
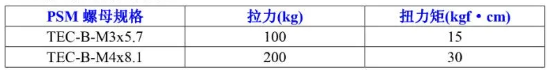
3.5 and 3.6: Torque and Pull-Out Strength Values for Hot-Press and Pre-Embedded Nuts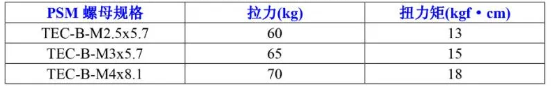
Chapter 4: Ultrasonic Embedding Process Overview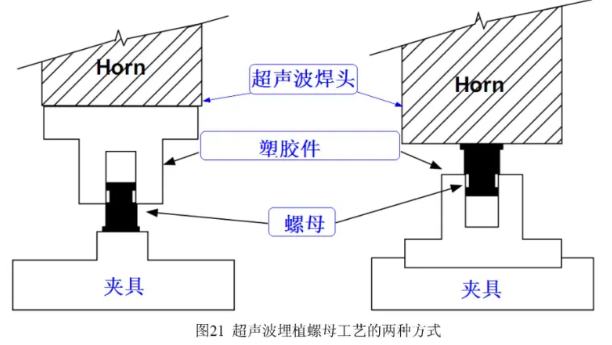
4.1 Advantages of Ultrasonic Embedding
- Short cycle time
- Low residual stress
- Multiple nuts can be embedded at once
- Suitable for high-melting materials
4.2 Ultrasonic Embedding Requirements
- Power Requirements: Based on nut diameter.
- Welding Head: Hard steel or surface-treated titanium for durability.
- Area: Welding head surface area should be 3-4 times the nut surface area.
- Support: Ensure good support and positioning of the plastic part.
