The drop test principle is to drop the package from a specified height onto a hard, flat surface to provide a means for evaluating the package's ability to withstand vertical impacts and the protection afforded by the packaging to the contents. Normally, product drop testing includes the following kinds of drop tests:
One is the drop test without any packaging, for the drop resistance characteristics of the product itself. It shall be decided based on the need of this test depending upon the characteristics of the product. For example, a fragile natural product that involves glass will not be asked to undergo this test.
The other is the drop test with packaging, which tests the protective performance during handling, transportation, and delivery, to ensure that the goods are received by the customer intact. The standards for the drop test of packaged products generally refer to the requirements of customers and sales area technical regulations or choose test conditions based on different ways of transportation. This shall be dealt with in accordance with the actual situation—single-wing drop tester.
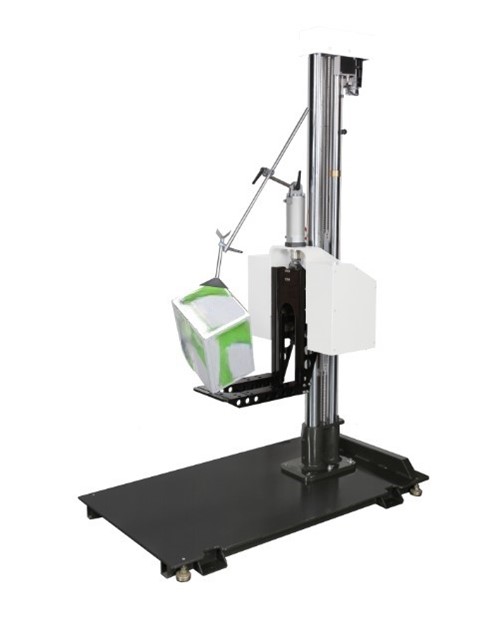

According to GB/T 2423.7-95 "Environmental Testing for Electrotechnical Products Part 2: Test Methods - Tilt and Topple Test"; GB/T 2423.8-95 "Environmental Testing for Electrotechnical Products Part 2: Test Methods - Free Fall Test" for drop tests.
There are national standards for drop tests, and the methods of drop include free fall on one corner, three edges, and six faces. The height of free fall shall be decided based on the weight of the product, which is classified into several grades: 90cm, 76cm, and 65cm.
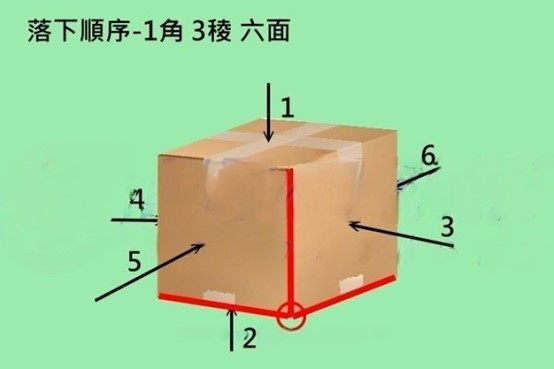
The droping steps
| Package Weight (lbs)/(㎏) | Drop Height (inches)/(㎝) |
| 1~20.99 lbs (0.45~9.54㎏) |
30 in (76.20㎝) |
| 21~40.99 lbs (9.55~18.63㎏) |
24 in (60.96㎝) |
| 41~60.99 lbs (18.64~27.72 ㎏) |
18 in (45.72㎝) |
| 61~100 lbs (17.73~45.45㎏) |
12 in (30.48㎝) |
Maximum displacement 25mm P-P.
